Even though 5G (or fifth generation cellular network) communication systems have only recently been deployed and the technology is still in its early stages, it is revolutionizing the way people connect with the world around them, enabling faster internet speeds and more reliable connectivity. Even so, the research into its successor, 6G (or sixth generation wireless mobile system standard), is well underway and is expected to become available early in the 2030s.
6G technology is expected to offer even faster data transfer speeds, lower latency, higher bandwidth, and more reliable connectivity than 5G. In this blog, we will explore the current and future status of 6G, including the potential features, challenges, and timeline for the technology.
6G’s Current State
It is important to remember that 6G is not yet a functioning technology. 6G is still in the early stages of development, and research and development are currently underway around the world. Many companies and organizations are investing in research to develop 6G, and some countries have already started planning to develop the technology.
It is difficult to predict the exact timeline for 6G, as the technology is still in the early stages of development. However, some estimates suggest that it could be commercially available around 2030. This timeline is based on the assumption that the technology will continue to advance at a rapid pace, and that significant investments will be made in research and development.
Many countries have already started planning for the development of 6G, including China, South Korea, and Japan. In China, the government has established a 6G research and development center, which is focused on developing the technology and infrastructure required for 6G. In South Korea, the government has launched a 6G task force, which is focused on developing the technology and standardization process. Recently, the U.S. House of Representatives reintroduced the Future Uses of Technology Upholding Reliable and Enhanced (FUTURE) Networks Act that directs the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) to bring together industry leaders, public interest groups, and government experts to establish a 6G task force.
6G Benefits
The market for 6G technology is predicted to enable significant advancements in imaging and location awareness. Working in conjunction with artificial intelligence (AI), the 6G infrastructure will be able to locate the best places for computing, and data storage, processing and sharing.
Further, many research papers have proposed various technologies and approaches for 6G. Some of the key advancements facilitated by 6G include cell-free massive MIMO, holographic communications, optical/visible light communications, terahertz frequency networks, and the use of edge artificial intelligence and machine learning to optimize network performance and efficiency.
Cell-free massive MIMO is an important core technology of 6G networks that may provide a solution to enhance the coverage and efficiency of wireless transmission.
Holographic communications have the potential to transform the way people communicate with each other. People will be able to create and share three-dimensional representations of themselves in real time. This technology could be used for virtual meetings, remote surgeries, and other applications.
Optical/visible light communication (VLC) has been recognized as a possible solution to increase data rates and system capacity in 6G networks. It offers high spectrum bandwidth in the range of 430 THz to 790 THz.
Terahertz frequency networks are another potential feature of 6G, and they could enable faster data transfer speeds and higher bandwidth. Terahertz frequency networks operate at frequencies between 300 GHz and 3 THz, which is significantly higher than the frequencies used in 5G technology. This means that terahertz frequency networks could enable faster data transfer speeds and higher bandwidth. Current projections call for 6G to be 100 times faster than 5G. Samsung Electronics recently tested 6G tech at 50 times faster than 5G.
The use of artificial intelligence and machine learning to optimize network performance and efficiency is another potential feature of 6G. With AI and machine learning, networks can be optimized to provide better connectivity, faster speeds, and more reliable service. This could lead to a more efficient and effective wireless network. The 6G environment is expected to revolutionize transportation/infrastructure, manufacturing, agriculture, healthcare, energy and entertainment.
6G Challenges
While 6G represents an exciting future for wireless technology, there are still technical and regulatory challenges that need to be addressed before the technology can become a reality. Some of the key challenges of 6G include:
Technical Challenges
One of the biggest technical challenges for 6G is developing the technology to operate at terahertz frequencies. Terahertz frequencies are significantly higher than the frequencies used in 5G technology and could provide ultra-high speeds and huge capacity over short distances. However, terahertz frequencies are highly susceptible to interference from environmental factors, such as water vapor and atmospheric gases, which can degrade the quality of the signal. Then there is the challenge of managing space requirements within devices for multiple wireless chips.
Infrastructure Challenges
Another challenge of 6G is developing the infrastructure to support the technology. 6G will require new cell towers, base stations, and other equipment. In addition, the infrastructure will need to be developed to support the higher frequencies used in 6G, which will require a significant amount of research and development.
Regulatory/Security Challenges
There are also significant regulatory challenges associated with 6G. Many countries around the world are still in the process of developing regulations for 5G. It will likely take several years for countries to develop regulations for 6G. In addition, there are significant privacy and security concerns associated with 6G, which will need to be addressed by regulators. For example, because 6G is intended to be a more open network than 5G, current security measures will not be powerful enough to protect the network from outside intruders. New security systems will need to be developed that can quickly detect and eliminate threats.
Research Initiatives and Key Players of 6G Technology
Research initiatives into 6G are becoming more popular as governments around the world are eager to embrace new technology ahead of rivals, most notably between the United States and China. According to China, they have already put a 6G experimental satellite into orbit. CNIPA (China National Intellectual Property Administration) announced that it owns 35% of the world’s 38,000 patents related to 6G.
As for the U.S., the 6G effort is primarily in the private sector. The U.S. National Science Foundation has partnered with other federal agencies and private industry to form RINGS — the Resilient and Intelligent Next-Generation Systems program and is funding projects worth $40 million. U.S. mobile companies are investing in their own 6G development. Notably, AT&T, Verizon, and T-Mobile are in charge of the Next G Alliance, an industry collaboration with ATIS, to help organize and accelerate 6G research in North America.
In Europe, research activity is well underway, aided by funding to the tune of €100 million and joint-initiatives like the EU-funded Hexa-X with contributions from the likes of Nokia and Ericsson.
The 6G Patent Landscape
It is generally accepted that patent filing trends are a key indicator of R&D investment and technological innovation. Further, the patent landscape will have to be navigated by all the players who wish to benefit from 6G technologies. MaxVal conducted a review of the 6G enabling technologies and applications to determine patent filing activity and provide a glimpse into the key players and technology trends in the 6G space.
Generally, 6G-related filings exploded in 2018 and all indications are that filings in this space will continue to rise. These patents include core 6G enabling technologies as well as those related to 6G applications (FIG. 1).
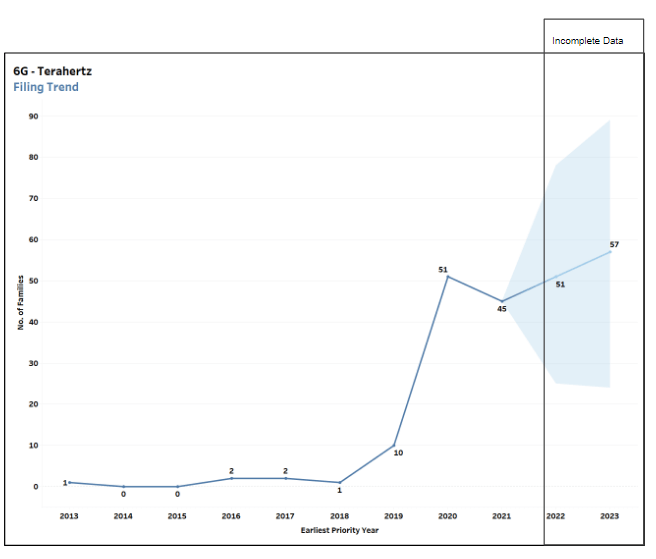
Fig. 1: This chart represents the filing trend in 6G space over the last 10 years (left). The filings related to terahertz also exhibit a similar trend (right). 2022-2023 data is incomplete due to publication lag.
China has outpaced the U.S. in 6G filings (see below).
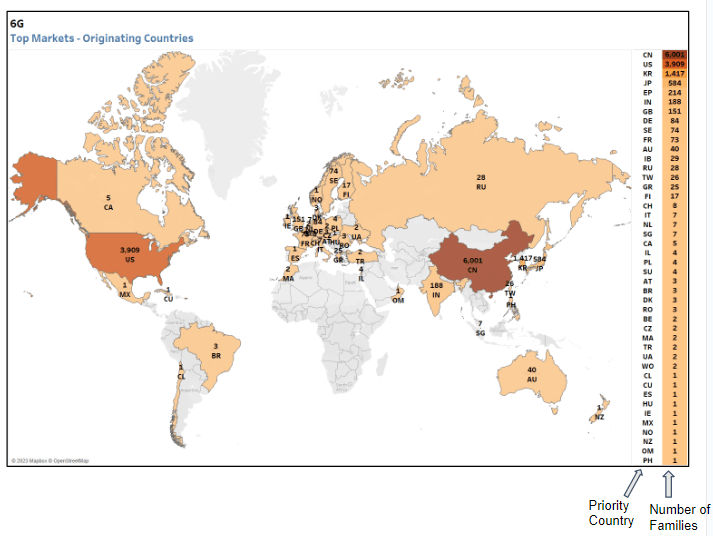
Fig. 2: This chart represents the first filings related to 6G in different jurisdictions (left). The filings related to terahertz also show most filings originate from China (right).
Interestingly, when looking at filing data and at a more granular level, while Huawei holds second place, first and 3rd place are held by South Korean companies, LG and Samsung Electronics. (see below).
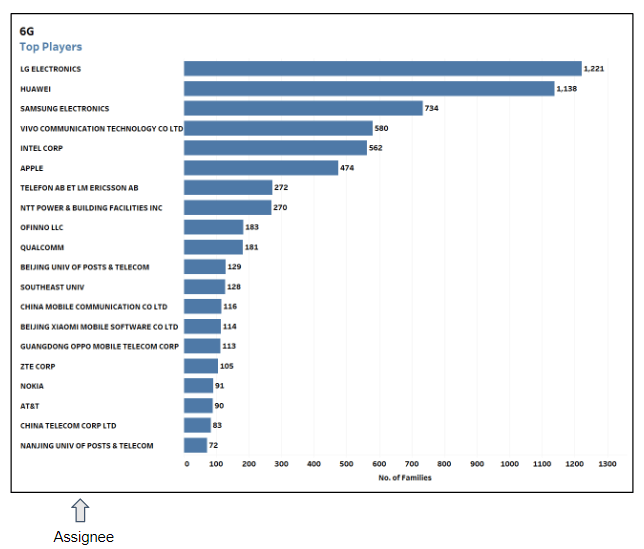
Fig. 3: This chart represents the top players in the 6G domain worldwide (left). The filings related to terahertz show different players focused on such enabling technologies (right).
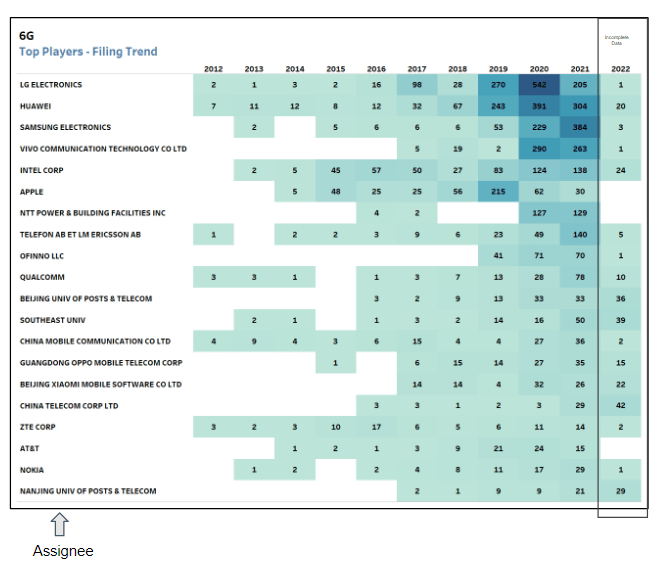
Fig. 4: This chart represents the filing trend of the top 20 assignees in the last 10 years (left). The below chart represents the top 20 assignees having families related to Terahertz in the last 10 years (right). 2022-2023 data is incomplete due to publication lag.
Conclusion
Despite these challenges, there is significant optimism and excitement surrounding the development of 6G. 6G represents an exciting future for wireless technology, with the potential to revolutionize the way people live and work. While it may be several years before the technology is commercially available, the potential benefits of 6G make it a technology worth investing in and exploring. As technology continues to advance, it is likely that 6G will play an increasingly important role in the way people connect with each other and the world around them.
Contact us for a complete patent landscape report on 6G technologies. Visit our Patent Search and Analytics page to explore our prior art and other search services.




