Smartphone design has gone through multiple iterations since the introduction of the first iPhone in 2007. A large touch screen has become the central focus providing visual output along with touch input. Designs have also moved towards increasing the screen to body ratio to keep the overall size of the device small while maximizing the display real estate.
In attempts to further increase this ratio, the smartphone industry appears to have zeroed in on two different approaches. The first has been to make the display foldable/expandable (See our earlier coverage related to foldable displays here). The other approach is to move all the front-facing sensors from non-screen areas (e.g. the bezel) to under screen. This integrated approach is called a bezel-less design.
There are two major types of fingerprint sensors: optical sensors, and ultrasonic sensors. Optical sensors rely on capturing an image of the fingerprint for authentication using light but can only read through glass. Ultrasonic sensors rely on ultrasonic sound for mapping the user’s fingerprint, which can be used through glass, plastic, or even metal. Under-screen (also in-screen or on-screen) fingerprint sensors providing biometric security have already become a staple feature in premium smartphones. In the near future, we can expect authentication by placing the finger anywhere on the phone and even devices that provide continuous authentication for improved security.
Image sensors may be the limiting factor for smartphone manufacturers looking into making a seamless all-screen bezel-less device. Image sensors are bulky and require a comparatively large amount of light to work satisfactorily. Other traditional front-facing sensors, such as proximity sensors and ambient light sensors can be replaced using software and inputs from the display and front-facing camera. A microphone can theoretically be positioned behind the display with sound guides that take up very little space. Further, the display itself can be converted to a piezoelectric vibrating speaker for audio output. The primary challenge for engineers integrating an image sensor under or into the display is balancing minimum light transmittance values for image capture while providing the display with an acceptable pixel density.
Patents can provide us with a glimpse into existing capabilities and future possibilities. To identify the patents and applications related to under-display image sensors, we extracted all the patents and applications related to image sensors and under-display arrangement. As can be seen from the application trends of the technology below, research and development of in-display cameras began fairly recently and is experiencing a rapid increase in patent filings since 2018.
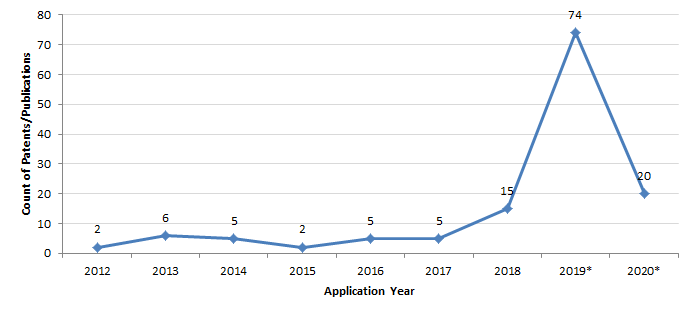
*incomplete due to publication lag Figure 1: Application year trends of the patents/publications worldwide related to image sensors into or under the display |
The graph below indicates that Chinese technology companies and display manufacturers may be leading in terms of global patent filings for integrating imaging sensors under the screen.
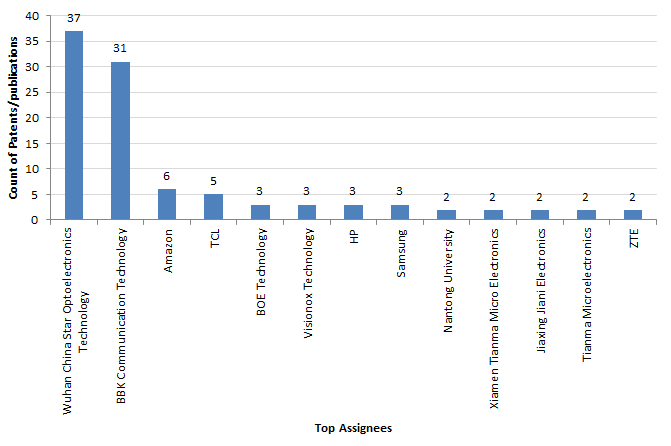
Figure 2: Top assignees based on their worldwide patents/applications related to in-display image sensors |
The current leaders are Wuhan China Star Optoelectronics Technology Co. Ltd and BBK communication technology which manufactures and sells smartphone devices under Realme, Oppo, Vivo, OnePlus, and iQOO brands. Samsung is one of the leading manufactures of the OLED and AMOLED displays. It also appears to have a minor stake in the Chinese display manufacturer, Wuhan China Star Optoelectronics Technology (Source: link), while TCL seems to own a 40% majority stake in Wuhan China Star Optoelectronics Technology with plans to increase the percentage of ownership in it with the induction of $588 Million into the company (Source: link). Our data indicates that heavy-weights in CMOS image sensor manufacturing, such as Sony and Omnivision currently do not have significant patents in this space.
Analysis of the patents reveals that the inventions focus on solving the light transmittance problem through a high pixel density display to an image sensor and not on the image sensor design itself. The majority of the patents in the overall portfolio are similarly related to display technologies and manufacturers. Some of the recent patents/applications are described below.
US9057931B1 assigned to Amazon and titled “Display Integrated Camera” discloses a display (522) with light-emitting pixels (506) arranged in sequence with microlenses (508, 510) for allowing incoming light to pass through the display, as shown in Figure 3. This particular arrangement of pixels and microlenses allows for an image sensor (528) to be integrated/stacked under the display module and still receives a sufficient amount for light to generate an image.
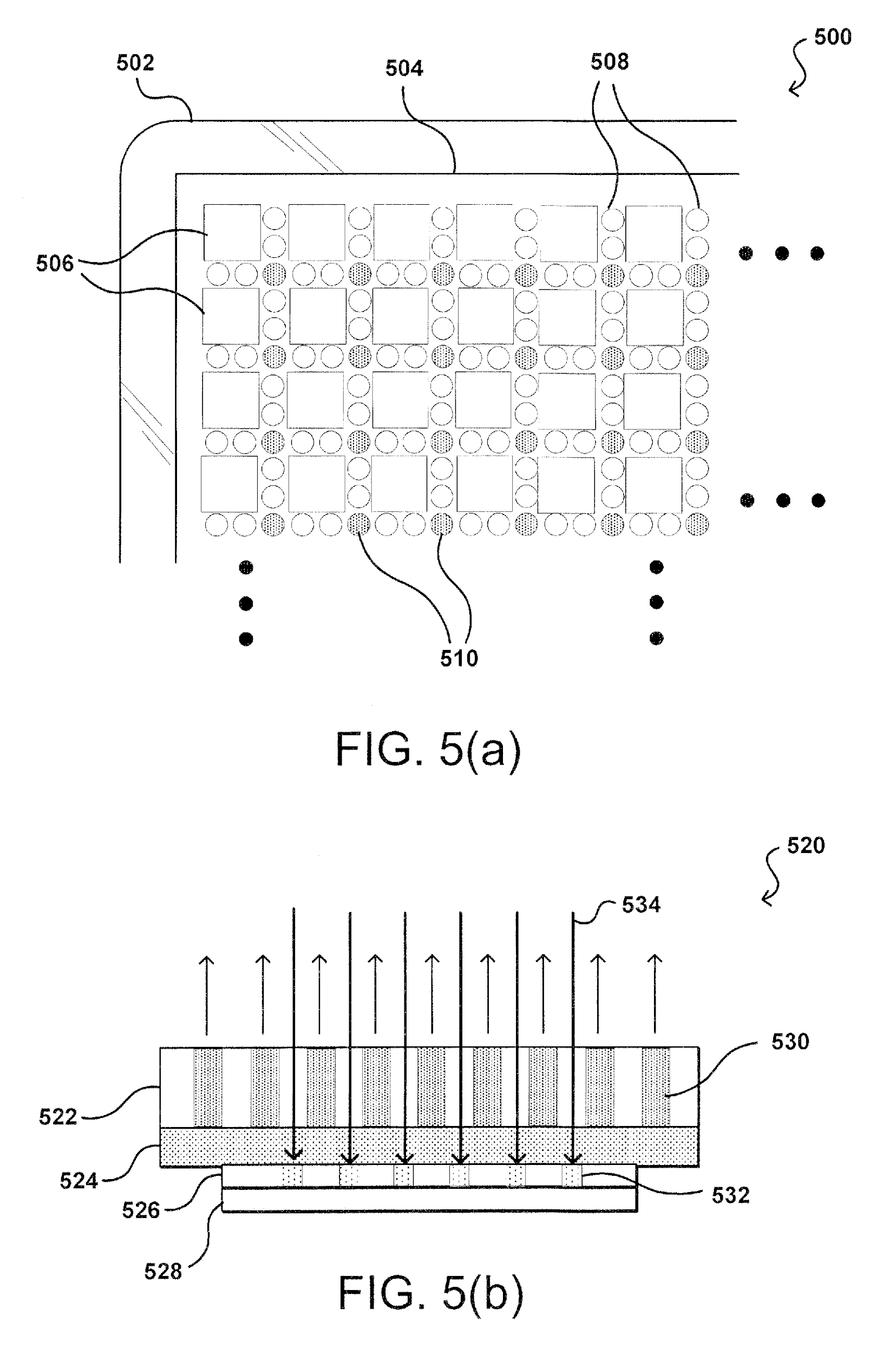 |
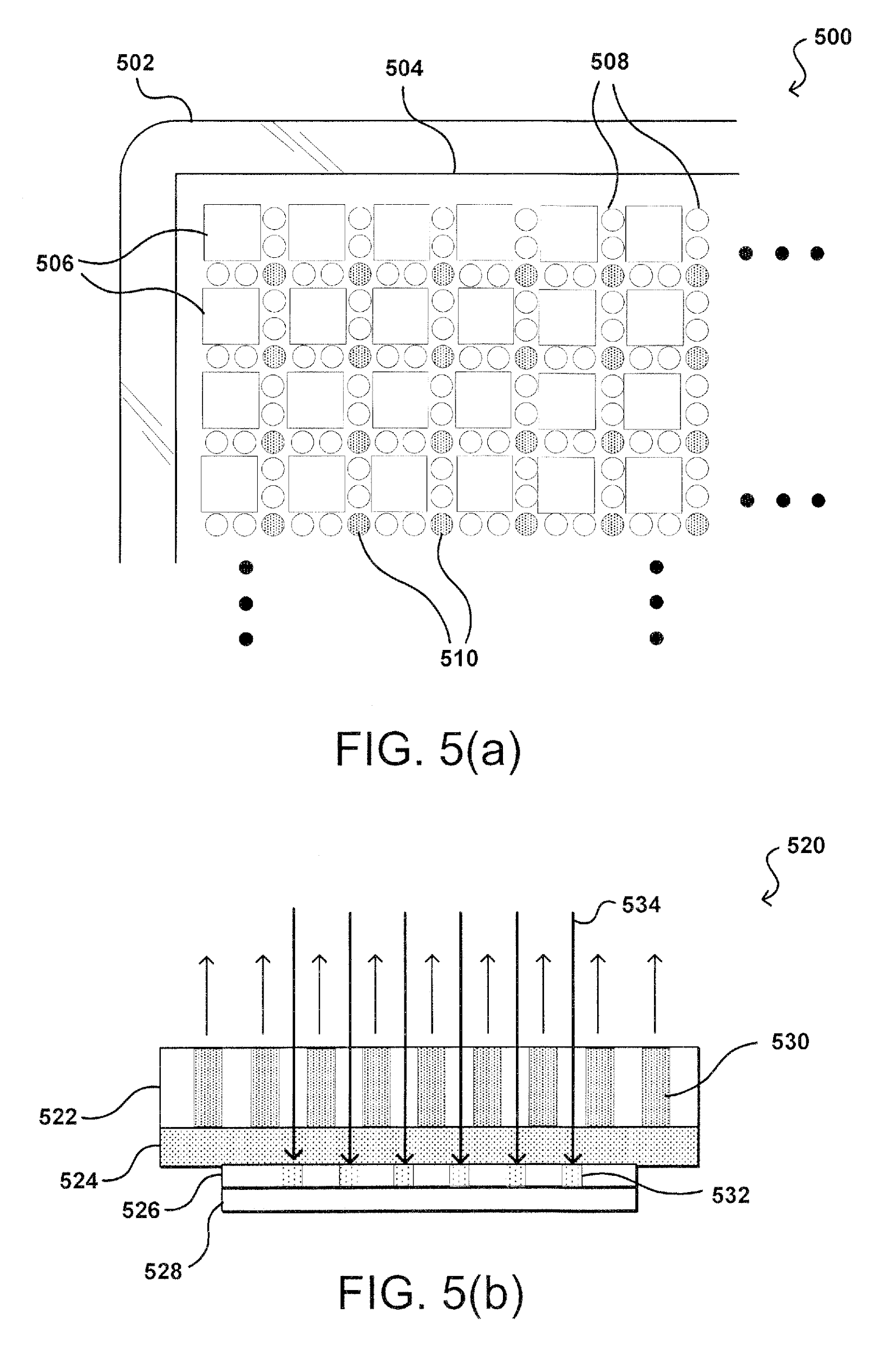 |
| Figure 3: US9057931B1 assigned to Amazon | |
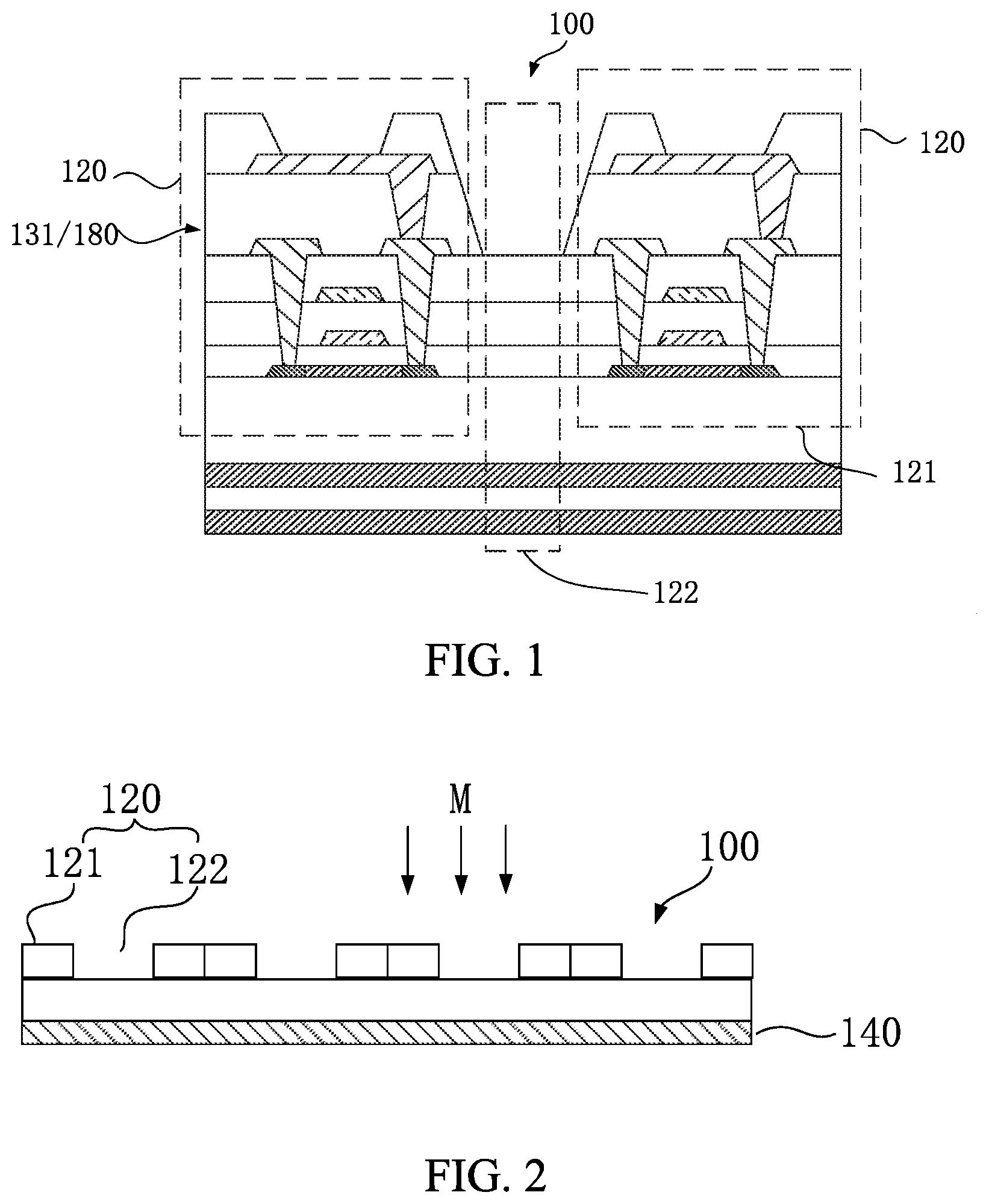
US20200211443A1 assigned to Wuhan China Star Optoelectronics Technology (Parent company: TCL) and titled “Display Panel and Display Device” is similar to the previous Amazon patent in that it is also focusing on pixel arrangement to allow increased light transmittance from the display to an image sensor at the back of the device, albeit in a different arrangement where the pixels and light-transmissive regions are denoted with 121 and 122 respectively (Figure 4).
 |
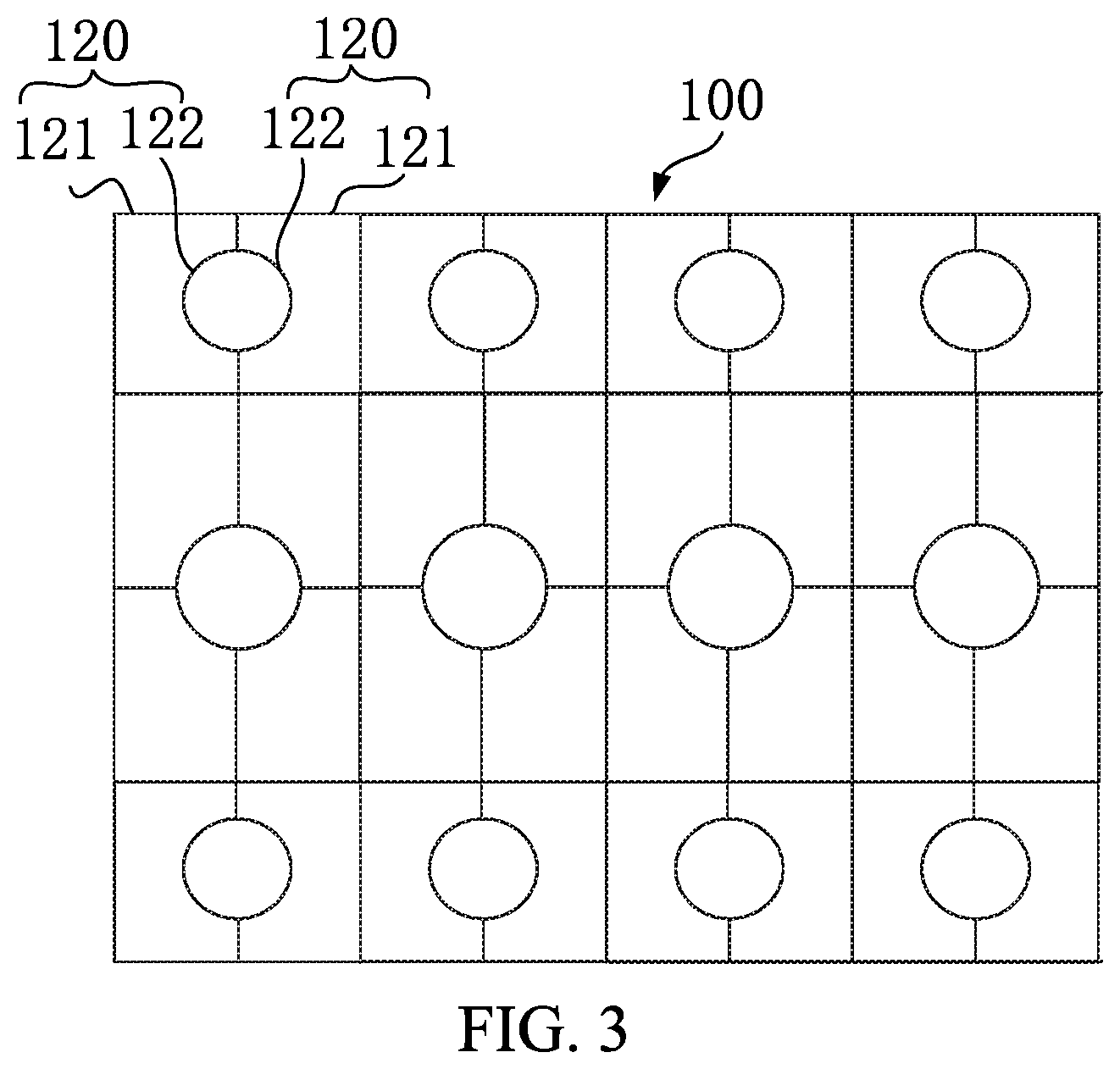 |
| Figure 4: US20200211443A1 assigned to Wuhan China Star Optoelectronics Technology | |
US9756257B2 assigned to HP and titled “Camera Included in Display” is another patent similar to the above two examples. However, the problem being addressed in this patent has less to do with increasing light transmittance through the display and more on light cross-talk resulting from emissions of the display pixels present in the camera region. To reduce cross-talk, the patent proposes a method where the display switches to a camera mode when using the camera during which the pixels in the region surrounding the camera module are dimmed (Figure 5).
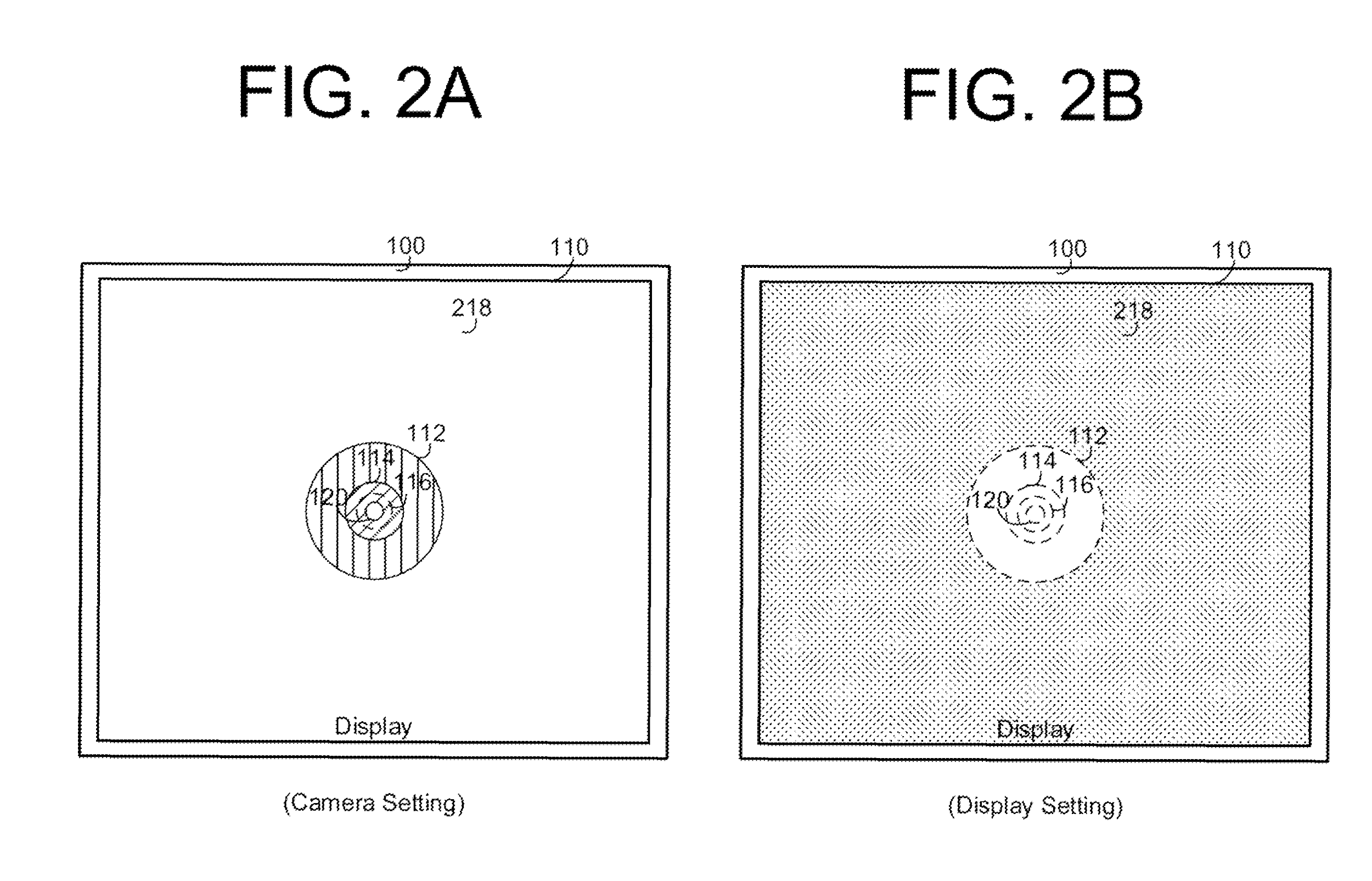
Figure 5: US9756257B2 assigned to HP |
The majority of patents in this space are owned by Chinese manufacturers. Research and development activity related to the under/in-display image sensors is relatively recent. However, a few smartphone manufacturers like Xiaomi and Oppo have already released plans for devices incorporating the described features (Source: link). Other than the fact that the technology problem exists, it is too early to predict with certainty whether research in this space will continue to rise or not. It is safe to say that the probability of a device with an in-display camera being commercialized soon is high.
To learn more about MaxVal’s Search and Analytics services. It is a great way to provide the most accurate and timely intellectual property information. With in-depth search capabilities and detailed reporting, this system allows IP professionals to quickly identify, analyze and protect value-adding opportunities for their business.